Beginner Course
Intermediate Course
Advanced Course7. IntensitySome analytic solutions such as Mie scattering are obtained as standing waves. We can calculate the standing wave in the simulation, but it is difficult to compare the result with the analytic solution due to phase shift. Here we introduce how to calculate time-independent intensity. The electromagnetic oscillation for a monochromatic wave is given by, ψ(r, t) = Aei(r⋅r±ωt) where A is the wave amplitude. From the real part of ψ(r, t), the imaginary part is given by Using the S- and NS-FDTD algorithms, we obtain 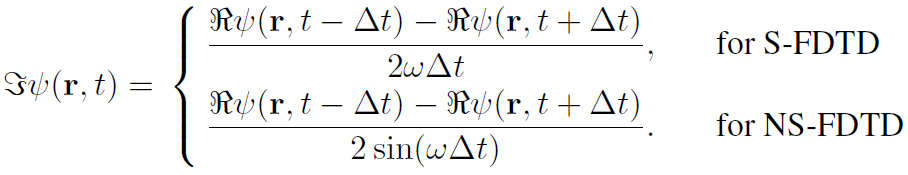 . . . (2) . . . (2)Hence the intensity distribution is given by where ψ(r, t)* is the complex conjugate.
Copyright (C) 2011 Naoki Okada, All Rights Reserved.
|